Atomic Number: 8 Atomic Mass: 15.9994 amu Melting Point:-218.4 °C (54.750008 K, -361.12 °F) Boiling Point:-183.0 °C (90.15 K, -297.4 °F) Number of Protons/Electrons: 8 Number of Neutrons: 8 Classification: Non-metal Crystal Structure: Cubic Density @ 293 K: 1.429 g/cm 3 Color: colorless Atomic Structure. Follow us at: The number of protons in the nucleus of an atom determines an element's atomic number. In other words, each. The number of protons determines an element’s atomic number (Z) and distinguishes one element from another. For example, carbon’s atomic number (Z) is 6 because it has 6 protons. The number of neutrons can vary to produce isotopes, which are atoms of the same. Electronegativity according to Pauling. 2.07 g.cm-3 at 20 °C.
Atomic Number of Sulfur is 16.
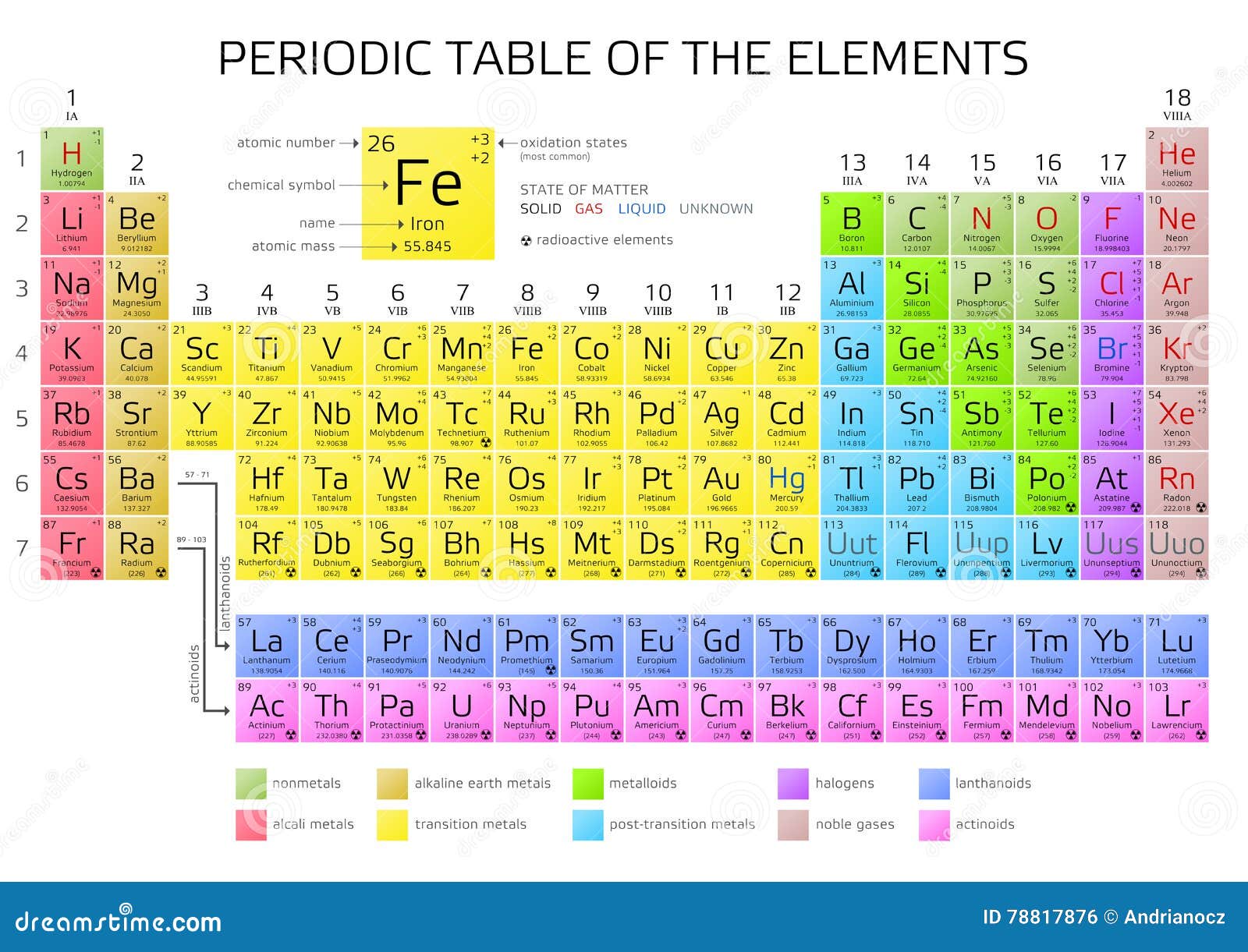
Chemical symbol for Sulfur is S. Number of protons in Sulfur is 16. Atomic weight of Sulfur is 32.06 u or g/mol. Melting point of Sulfur is 113 °C and its the boiling point is 444,7 °C.
» Boiling Point» Melting Point» Abundant» State at STP» Discovery YearAbout Sulfur
Sulfur is a yellowish crystal-solid substance and a nonmetal. It is essential for all living things on our planet. Sulfur can be taken up from natural sources and it plays an important role for creating various amino acids. It is believed that its name has Sanskrit roots. This chemical element easily enters the reaction with oxygen and produces quite unpleasant odor. It also quickly takes soft rubbery form known as plastic sulfur. Sulfur produces a large number of chemical compounds, which include acids, oxides, sulfates, sulfites, sulfides, and others. They are extensively used in chemical industry, namely for producing fertilizers, fungicides, food preservatives, detergents, and so on. Besides, the most important uses of this chemical element include medicine, gunpowder production, producing some household goods, etc. Sulfur can be found in minerals, salts, etc., which are usually in abundance in various volcanic regions.

Properties of Sulfur Element
| Atomic Number (Z) | 16 |
|---|---|
| Atomic Symbol | S |
| Group | 16 |
| Period | 3 |
| Atomic Weight | 32.06 u |
| Density | 2.067 g/cm3 |
| Melting Point (K) | 388.36 K |
| Melting Point (℃) | 113 °C |
| Boiling Point (K) | 717.87 K |
| Boiling Point (℃) | 444,7 °C |
| Heat Capacity | 0.71 J/g · K |
| Abundance | 350 mg/kg |
| State at STP | Solid |
| Occurrence | Primordial |
| Description | Non-metal |
| Electronegativity (Pauling) χ | 2.58 |
| Ionization Energy (eV) | 10.36001 |
| Atomic Radius | 100pm |
| Covalent Radius | 102pm |
| Van der Waals Radius | 180 |
| Valence Electrons | 6 |
| Year of Discovery | prehistoric |
| Discoverer | unknown |
What is the Boiling Point of Sulfur?
Sulfur boiling point is 444,7 °C. Boiling point of Sulfur in Kelvin is 717.87 K.
What is the Melting Point of Sulfur?
Sulfur melting point is 113 °C. Melting point of Sulfur in Kelvin is 388.36 K.
How Abundant is Sulfur?
Abundant value of Sulfur is 350 mg/kg.
What is the State of Sulfur at Standard Temperature and Pressure (STP)?
State of Sulfur is Solid at standard temperature and pressure at 0℃ and one atmosphere pressure. Batman arkham city alternate costumes.
When was Sulfur Discovered?
Sulfur was discovered in prehistoric.
Learning Objective
- Determine the relationship between the mass number of an atom, its atomic number, its atomic mass, and its number of subatomic particles
Key Points
- Neutral atoms of each element contain an equal number of protons and electrons.
- The number of protons determines an element’s atomic number and is used to distinguish one element from another.
- The number of neutrons is variable, resulting in isotopes, which are different forms of the same atom that vary only in the number of neutrons they possess.
- Together, the number of protons and the number of neutrons determine an element’s mass number.
- Since an element’s isotopes have slightly different mass numbers, the atomic mass is calculated by obtaining the mean of the mass numbers for its isotopes.
Terms
- atomic massThe average mass of an atom, taking into account all its naturally occurring isotopes.
- mass numberThe sum of the number of protons and the number of neutrons in an atom.
- atomic numberThe number of protons in an atom.
Atomic Number
Neutral atoms of an element contain an equal number of protons and electrons. Tidal deezer qobuz. The number of protons determines an element’s atomic number (Z) and distinguishes one element from another. For example, carbon’s atomic number (Z) is 6 because it has 6 protons. The number of neutrons can vary to produce isotopes, which are atoms of the same element that have different numbers of neutrons. The number of electrons can also be different in atoms of the same element, thus producing ions (charged atoms). For instance, iron, Fe, can exist in its neutral state, or in the +2 and +3 ionic states.
Mass Number
An element’s mass number (A) is the sum of the number of protons and the number of neutrons. The small contribution of mass from electrons is disregarded in calculating the mass number. This approximation of mass can be used to easily calculate how many neutrons an element has by simply subtracting the number of protons from the mass number. Protons and neutrons both weigh about one atomic mass unit or amu. Isotopes of the same element will have the same atomic number but different mass numbers.

Scientists determine the atomic mass by calculating the mean of the mass numbers for its naturally-occurring isotopes. Often, the resulting number contains a decimal. For example, the atomic mass of chlorine (Cl) is 35.45 amu because chlorine is composed of several isotopes, some (the majority) with an atomic mass of 35 amu (17 protons and 18 neutrons) and some with an atomic mass of 37 amu (17 protons and 20 neutrons).
Given an atomic number (Z) and mass number (A), you can find the number of protons, neutrons, and electrons in a neutral atom. For example, a lithium atom (Z=3, A=7 amu) contains three protons (found from Z), three electrons (as the number of protons is equal to the number of electrons in an atom), and four neutrons (7 – 3 = 4).
Show SourcesBoundless vets and curates high-quality, openly licensed content from around the Internet. This particular resource used the following sources:
http://www.boundless.com/
Boundless Learning
CC BY-SA 3.0.

http://en.wiktionary.org/wiki/atomic_number
Wiktionary
CC BY-SA 3.0.
http://www.boundless.com//biology/definition/atomic-mass–2
Boundless Learning
CC BY-SA 3.0.
Atomic Number Of Sg
http://en.wikibooks.org/wiki/A-level_Chemistry/OCR/Atoms,_Bonds_and_Groups/Atoms_and_Reactions/Atoms
Wikibooks
CC BY-SA 3.0.
Sulfur Number Of Electrons
Atomic Number Of Strontium
http://cnx.org/content/m44390/latest/?collection=col11448/latest
OpenStax CNX
CC BY 3.0.
Definition: A fashion croqui term (originated from a french word “croquis” meaning “rough sketch”) in fashion design is referred to an outlined fashion sketch of a figure model in various poses that fashion designers use as a template for fashion sketching and drawing, to illustrate and present fashion designs. In fashion, a croquis is a quick sketch of an ensemble. These expressive fashion illustrations bring an artist’s design to life.  Feb 27, 2021 - Explore Cathy Starr's board 'Croquis', followed by 912 people on Pinterest. See more ideas about fashion figures, fashion drawing, fashion sketches. Nov 18, 2019 - Vector fashion design templates for sketching and tracing designs on Successful Fashion Designer Fashion croquis, poses and templates for fashion design drawing and sketches #fashionsketches #croquis #fashiondesign #fashiondesigner. See more ideas about fashion design template, fashion sketches, fashion design. Draw the fashion croquis using the attached guidelines by following these steps: 1) Print the attached page or create guidelines by following the steps in video #4 2) Create the skeleton of the croquis by following the steps in video #5 3) Add muscular shape to the croquis by following the steps in video #6.
Feb 27, 2021 - Explore Cathy Starr's board 'Croquis', followed by 912 people on Pinterest. See more ideas about fashion figures, fashion drawing, fashion sketches. Nov 18, 2019 - Vector fashion design templates for sketching and tracing designs on Successful Fashion Designer Fashion croquis, poses and templates for fashion design drawing and sketches #fashionsketches #croquis #fashiondesign #fashiondesigner. See more ideas about fashion design template, fashion sketches, fashion design. Draw the fashion croquis using the attached guidelines by following these steps: 1) Print the attached page or create guidelines by following the steps in video #4 2) Create the skeleton of the croquis by following the steps in video #5 3) Add muscular shape to the croquis by following the steps in video #6.
